When you think about the broad landscape of Islam, you quickly realize it is that, a faith practiced by a vast number of people across the globe. It's a bit like looking at a huge, beautiful garden, with many different kinds of flowers all growing from the same rich soil. In the same way, the Islamic faith, which is followed by about 1.6 billion people around the world right now, has a couple of very large branches that, while sharing a common root, have developed their own distinct paths over time. This makes it really interesting to explore how these different expressions of faith exist, especially when we consider places like Iran, where one of these branches is very prominent, more or less shaping much of the country's identity.
You see, at its heart, the division between what we call Sunni and Shia Muslims isn't about the basic beliefs of Islam itself. Both groups, as a matter of fact, believe in the oneness of God, they accept Muhammad as the final prophet, and they hold the Holy Quran as their sacred scripture. They also share the fundamental theological ideas of Islam, so there is a deep, underlying unity in their faith. What sets them apart, fundamentally, is more about a historical disagreement, a kind of divergence that happened a very long time ago, concerning who should have led the Muslim community after Prophet Muhammad passed away.
This historical point, this particular moment in time, has truly shaped the way these two groups have developed, influencing their practices, their interpretations, and even their geographical distribution across the world. While most Muslims globally are Sunni, there are, as it happens, a handful of countries where Shia Muslims form a very significant part of the population, or even the majority. Iran, of course, is one of those places, and understanding the nuances of the Shia and Sunni population in Iran means first getting a feel for these historical threads and shared beliefs.
Table of Contents
- What Really Caused the Split Between Shia and Sunni Muslims?
- Shared Foundations - What Do Shia and Sunni Muslims Share in Iran?
- How Did Historical Events Shape Shia Identity and the Shia and Sunni Population in Iran?
- The Role of Imams in Shia Islam and Its Impact on the Shia and Sunni Population in Iran
- A Global Picture of the Shia and Sunni Population
- Exploring the Spiritual Depth of Shia Islam
- How Do Core Beliefs Influence the Shia and Sunni Population in Iran?
- Understanding the Branches of Islam
What Really Caused the Split Between Shia and Sunni Muslims?
The initial point of divergence, the moment that truly set these two paths apart, was, you know, a discussion about who should lead the Muslim community right after the passing of Prophet Muhammad. This wasn't about a disagreement on the message of Islam itself, but rather about the line of succession for leadership. The Shia, which is a word that means "party" or "followers" of Ali, held the conviction that Muhammad had, in fact, designated Ali ibn Abi Talib to be his successor. Ali, as it happens, was the Prophet's son-in-law and cousin, and those who would become Shia believed he possessed a special spiritual authority and a rightful claim to lead the community. This belief, this conviction, is quite central to their identity, even today, and it certainly plays a part in understanding the makeup of the Shia and Sunni population in Iran.
On the other hand, the group that would come to be known as Sunni Muslims, representing the larger part of the global Muslim community, believed that the leadership should pass to someone chosen by consensus of the community, not necessarily through a direct lineage from the Prophet. They felt that the most qualified person, someone who had the respect and trust of the community, should take the reins. This fundamental difference in how leadership should be determined is, arguably, the very origin point of the split. It's a political disagreement at its core, but it certainly led to distinct theological and historical paths for both groups.
So, you see, the disagreement was never about the core tenets of faith, but rather about the practical matter of governance and spiritual guidance after the Prophet's time. This historical moment, this choice of paths, meant that over centuries, the two branches developed slightly different ways of interpreting Islamic law, different traditions, and different narratives about their past. It’s a bit like two rivers that start from the same mountain spring but then flow in different directions, each carving its own course through the landscape. This early divergence, in a way, laid the groundwork for the unique characteristics you see in the Shia and Sunni population in Iran.
Shared Foundations - What Do Shia and Sunni Muslims Share in Iran?
Despite the historical differences concerning leadership, it's really important to remember that Shia and Sunni Muslims share a huge amount in common. They are, at the end of the day, both Muslims. This means they hold the same fundamental theological beliefs that form the very bedrock of Islam. For instance, both groups believe in the absolute oneness of God, a concept known as Tawhid. This is a core principle, a belief that there is no god but God, and it is something that absolutely unites all followers of Islam, regardless of their specific branch.
They also share a belief in prophethood, accepting that Muhammad is the final prophet sent by God to humanity. This includes the conviction that the Holy Quran is the literal word of God, revealed to Prophet Muhammad. Both Shia and Sunni Muslims look to the Quran as their ultimate guide for life, for spiritual wisdom, and for understanding the divine will. It's truly a shared sacred text, something that binds them together in a profound way.
Beyond these central tenets, both branches observe the five pillars of Islam, though there might be slight variations in practice or interpretation. These pillars include the declaration of faith, daily prayers, charitable giving, fasting during Ramadan, and the pilgrimage to Mecca if one is able. So, while you might observe some different customs or rituals in different places, the underlying acts of worship and devotion are, in fact, very much the same. This shared foundation is, you know, a powerful reminder of their common faith, and it is something that, in a way, bridges any historical divides within the Shia and Sunni population in Iran.
How Did Historical Events Shape Shia Identity and the Shia and Sunni Population in Iran?
The story of Karbala, for example, is a moment in history that is very, very central to Shia identity. It’s a powerful narrative, a tragic event that took place in the seventh century, where Imam Hussein, who was the grandson of Prophet Muhammad and a son of Ali, faced a terrible ordeal. This event, which involved immense sacrifice and suffering, became a defining moment for Shia Muslims. It really cemented their sense of identity, their feeling of connection to the Prophet's household, and their commitment to justice and standing up against what they see as oppression.
This historical narrative, this deep, emotional connection to Karbala, is not just a story from the past; it is, in fact, a living part of Shia spiritual life and identity. It has shaped their theological outlook, their philosophical traditions, and their understanding of martyrdom and sacrifice. The commemoration of this event, which happens annually, is a time of deep reflection and mourning for Shia communities around the world, and it is a truly powerful expression of their faith.
So, you see, these historical events, particularly Karbala, have played a huge role in shaping what it means to be Shia. They are not just dates on a calendar; they are moments that have deeply influenced the collective memory, the spiritual practices, and the very fabric of Shia communities. This historical journey, this unique path, is something that has, in a way, contributed to the distinct character of the Shia population wherever they are found, including, of course, the Shia and Sunni population in Iran.
The Role of Imams in Shia Islam and Its Impact on the Shia and Sunni Population in Iran
A very distinctive aspect of Shia Islam, one that sets it apart from Sunni Islam, is the significant role of the Imams. In Shia belief, the Imams are not just leaders in the conventional sense; they are seen as spiritual guides and successors to the Prophet Muhammad, possessing special knowledge and infallibility. The first of these Imams, of course, was Ali ibn Abi Talib, and the lineage continued through his descendants. This concept of divinely appointed spiritual leadership is, in a way, a cornerstone of Shia theology and practice.
These Imams are believed to be the authoritative interpreters of the Quran and the teachings of the Prophet. Their guidance is considered essential for truly understanding the deeper meanings of Islam and for navigating life's challenges. This reverence for the Imams, this belief in their unique spiritual status, is a very central part of Shia identity and religious life. It provides a distinct framework for their religious authority and their approach to faith.
The emphasis on the Imams also influences the structure of religious leadership and the way religious knowledge is transmitted within Shia communities. It creates a different kind of spiritual hierarchy and a different focus in their devotional practices compared to Sunni Islam. This focus on the Imams is, arguably, one of the key elements that distinguishes Shia Islam as a branch with its own rich spiritual and historical depth, and it certainly contributes to the unique character of the Shia and Sunni population in Iran.
A Global Picture of the Shia and Sunni Population
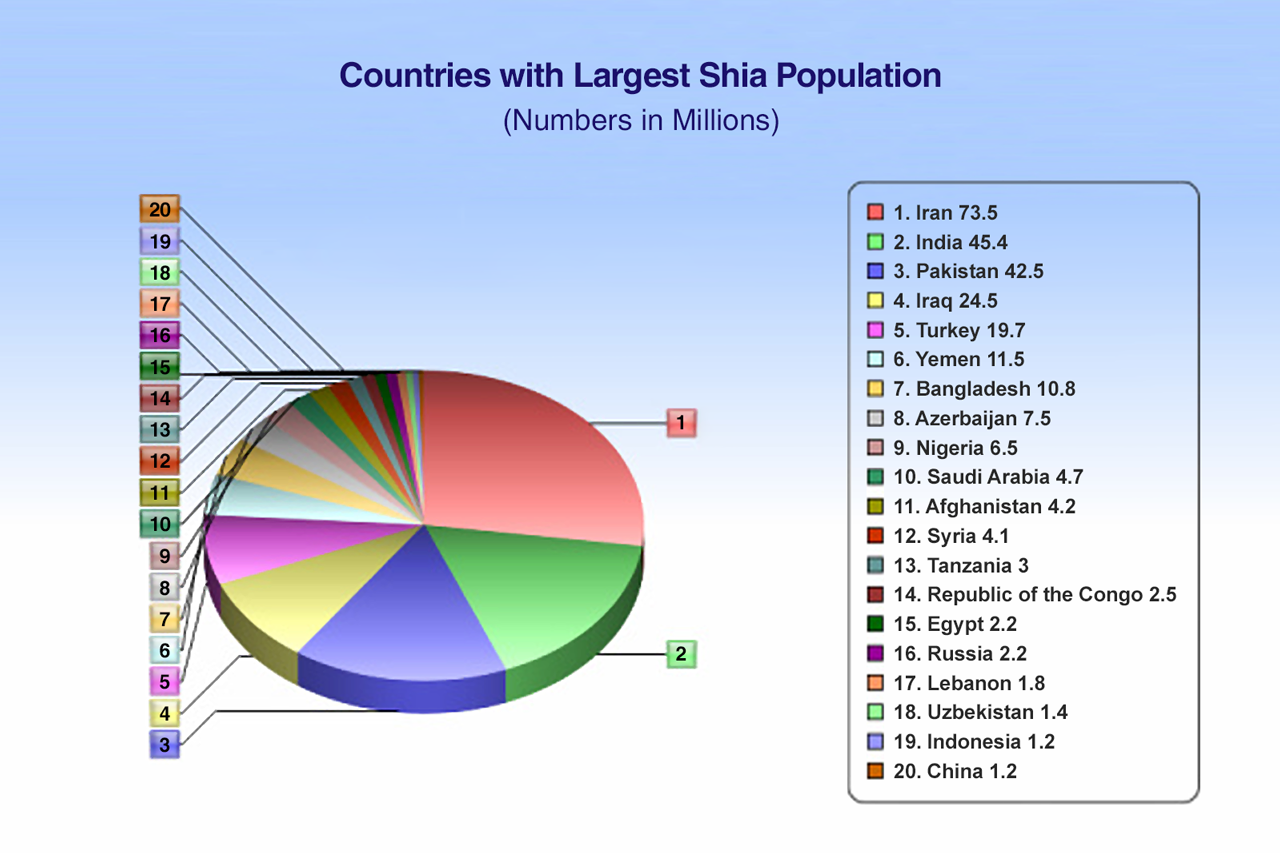
When we look at the numbers on a global scale, it's clear that the majority of the world's Muslims are Sunni. Out of the roughly 1.6 billion Muslims around the planet today, Shia Muslims account for nearly 20 percent. This means that while they are a significant group, they represent a smaller proportion of the total Muslim population worldwide. This global distribution is, in fact, quite interesting, as it shows how the two branches have spread and developed over centuries in different regions.
However, it's also true that while most global Muslims are Sunni, there are, in fact, a handful of countries where Shia Muslims make up a very large part of the population, or even the majority. These are places where Shia Islam has historically flourished and become the predominant form of the faith. This geographical concentration is, you know, a result of various historical, political, and social factors that have shaped the religious landscape of these nations over a long period.
So, when we talk about the Shia and Sunni population in Iran, we are discussing one of those specific countries where Shia Islam holds a very prominent place. It's one of the nations where the nearly 20 percent global figure for Shia Muslims is significantly represented. Understanding this global context helps us appreciate the particular religious makeup of Iran and how it fits into the broader Islamic world, offering a unique perspective on the dynamics of faith in different parts of the world.
Exploring the Spiritual Depth of Shia Islam
Shia Islam is, in fact, a deeply spiritual and historically rich branch of Islam. Its origins, as we have discussed, stem from that initial leadership debate, but its development has gone far beyond that political point. It has, over many centuries, developed a profound theological depth and a very rich philosophical tradition. This means that beyond the historical narrative, there is a whole world of spiritual thought and intellectual inquiry that defines Shia identity.
From its emphasis on the story of Karbala, which is, you know, a central narrative of sacrifice and justice, to its complex theological discussions about the nature of God, prophecy, and the role of human reason, Shia Islam offers a very unique spiritual path. It encourages its followers to engage with their faith on a deeper level, to seek out knowledge, and to reflect on the moral and ethical dimensions of their beliefs. This intellectual and spiritual engagement is, in a way, a hallmark of Shia thought.
To truly get a better sense of Shia Islam, it's really helpful to learn about its origins, its core beliefs, its practices, and the many contributions it has made to Islamic civilization. Discovering how historical events have shaped Shia identity, and examining the theological and philosophical aspects, helps paint a more complete picture. This spiritual richness is, arguably, a key component of what makes the Shia population distinct, and it certainly plays a role in the character of the Shia and Sunni population in Iran.
How Do Core Beliefs Influence the Shia and Sunni Population in Iran?
The core Islamic beliefs, which are shared by both Shia and Sunni Muslims, truly form the bedrock of their faith and practice, even within the context of the Shia and Sunni population in Iran. These fundamental beliefs, such as the oneness of God, the acceptance of Muhammad as the final prophet, and the Holy Quran as divine revelation, provide a common spiritual ground. It means that despite their historical differences, both groups pray to the same God, face the same direction for prayer, and recite from the same sacred text.
This shared theological foundation means that, in a very basic sense, a Shia Muslim is, you know, like any other Muslim when it comes to these core tenets. They share the fundamental theological beliefs of Islam, such as the oneness of God, the acceptance of prophethood, and the finality of Prophet Muhammad. This also includes their reverence for the Holy Quran. So, in their most basic acts of worship and belief, there is a deep and undeniable unity.
However, the subtle differences in interpretation, particularly around the concept of leadership and the role of the Imams, can lead to variations in religious practice and community organization. These differences, while not affecting the core belief in God or the Prophet, create distinct identities within the broader Islamic faith. This interplay of shared fundamental beliefs and specific interpretive paths is, in a way, what defines the religious landscape, including that of the Shia and Sunni population in Iran.
Understanding the Branches of Islam
To get a really good sense of the dynamics within the Shia and Sunni population in Iran, it is, in fact, helpful to understand that the distinction between these two major branches of Islam, the Shia and the majority Sunnis, stems from historical events. It’s not just a casual difference; it's rooted in significant moments that shaped the early Muslim community. This historical origin is, you know, key to appreciating why these two groups exist and how they have developed their distinct characteristics over time.
The origins of the split between the Sunnis and the Shia are, as we have seen, largely tied to political disagreements over leadership after Prophet Muhammad's passing. This disagreement, while political in nature, led to a branching off that eventually solidified into two distinct theological and jurisprudential traditions. It’s a bit like two different schools of thought emerging from the same foundational teachings, each with its own preferred method of interpreting and applying those teachings.
In this overview, we are exploring the basics of Shia Islam, going into its origins and history, discussing key beliefs and practices, and looking at the role of Imams. This helps shed light on how these distinctions came to be. Understanding these origins and the subsequent historical journey is, arguably, crucial for anyone wanting to grasp the full picture of the Shia and Sunni population in Iran, and indeed, the broader Islamic world.
Related Resources:

Detail Author:
- Name : Bonita Kuphal
- Username : rbradtke
- Email : vivienne.greenfelder@torp.net
- Birthdate : 1988-11-20
- Address : 10402 Alvera Mountain Suite 033 South Carolyne, AL 14358-1207
- Phone : 614-507-8033
- Company : Cummerata Group
- Job : Hazardous Materials Removal Worker
- Bio : Quas corrupti accusamus enim cumque vero harum. Dolorem atque accusantium possimus. Voluptas ipsam quam quia ut ut in ullam.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/lrath
- username : lrath
- bio : Ducimus consequatur cum molestiae voluptate. Nemo aut similique ratione aut ut aut.
- followers : 6639
- following : 1699
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/lawson_official
- username : lawson_official
- bio : Quod commodi quia omnis eligendi veniam. Et similique quia ut expedita et aliquid. Molestias vero vel saepe quaerat exercitationem dolores aut.
- followers : 2553
- following : 2549
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/lawson_rath
- username : lawson_rath
- bio : Nulla culpa mollitia animi et facere. Sit aut temporibus odio id.
- followers : 2235
- following : 1979